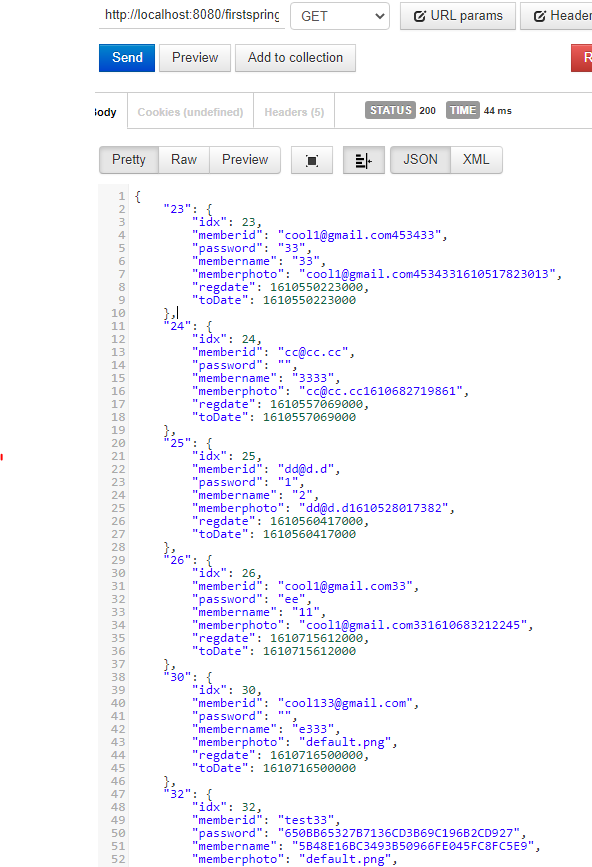
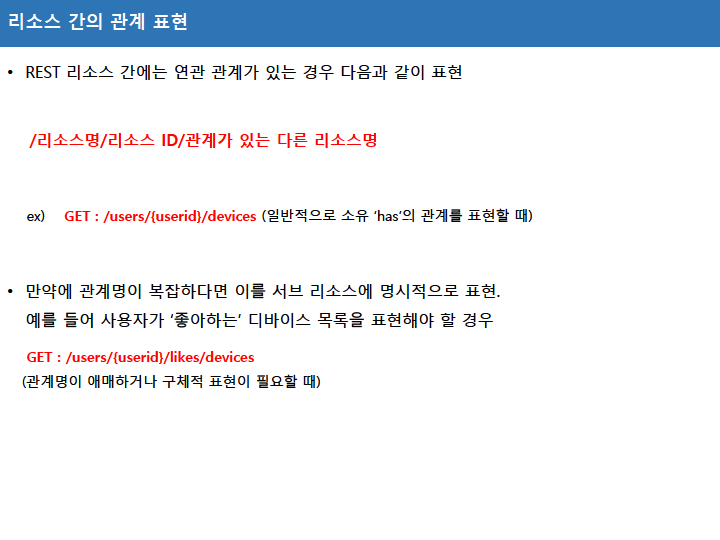
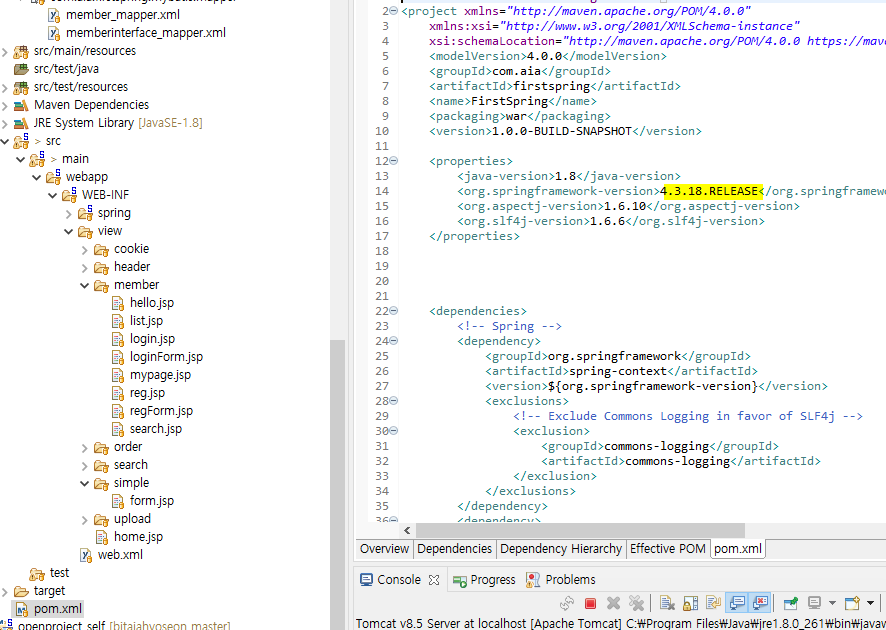
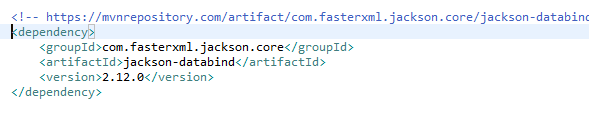
HTTP 통신 기반의 아키텍처 REST
REST API는 다음의 구성되어있다.
@PathVariable을 이용한 경로 변수 처리
- 경로의 특정 위치 값이 고정되지 않고 달라질 때 사용하는 것이 @PathVariable
@RequestBody & @ResponseBody
@RequestBody 과 @ResponseBody는 요청몸체와 응답 몸체 구현 - @RequestBody : JSON 형식의 요청 몸체를 자바 객체로 변환 - @ResponseBody : 자바 객체를 JSON 이나 XML 형식의 문자열로 변환 - Spring Framework는 HttpMessageConverter 를 이용해서 자바 객체와 HTTP 요청/응답 몸체 사이의 변환 처리
package com.aia.firstspring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mc/simple")
public class SimpleConvertercontroller {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String form() {
return "simple/form";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String simple(@RequestBody String body) {
System.out.println(body + " @ResponseBody 어노태이션은 일반객체도응답처리가된다 ");
return body;
}
}
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>form</h1>
<form method="post">
name : <input type="text" name="uname"><br>
age : <input type="number" name="age"><br>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
JAXB2를 이용한 XML 처리
package com.aia.firstspring.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.aia.firstspring.domain.GuestMessage;
import com.aia.firstspring.domain.GuestMessageList;
@Controller
public class GuestMessageController {
@RequestMapping("/message/listXml")
@ResponseBody
public GuestMessageList listXml() {
return getMessageList();
}
private GuestMessageList getMessageList() {
List<GuestMessage> list = new ArrayList<GuestMessage>();
list.add(new GuestMessage(1, "안녕", new Date()));
list.add(new GuestMessage(2, "HELLO", new Date()));
list.add(new GuestMessage(3, "빠이", new Date()));
return new GuestMessageList(list);
}
}package com.aia.firstspring.domain;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name="", propOrder = {"id", "message", "regDate"})
public class GuestMessage {
private int id;
private String message;
private Date regDate;
public GuestMessage() {
}
public GuestMessage(int id, String message, Date regDate) {
this.id = id;
this.message = message;
this.regDate = regDate;
}
}
package com.aia.firstspring.domain;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlRootElement(name="message-list") // <message-list></message-list>
public class GuestMessageList {
@XmlElement(name="message")
private List<GuestMessage> message;
public GuestMessageList(List<GuestMessage> message) {
this.message = message;
}
public List<GuestMessage> getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(List<GuestMessage> message) {
this.message = message;
}
public GuestMessageList() {
}
}
JACKSON2를 이용한 JSON 형식의 처리
잭슨 버전과 스프링 버전에 신경써서 해야함
package com.aia.firstspring.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.aia.firstspring.domain.GuestMessage;
import com.aia.firstspring.domain.GuestMessage2;
import com.aia.firstspring.domain.GuestMessageList2;
@Controller
public class GuestMessageController2 {
@RequestMapping(value= "/message/listJson")
@ResponseBody
public GuestMessageList2 listXml2() {
return getMessageList2();
}
private GuestMessageList2 getMessageList2() {
List<GuestMessage2> list2 = new ArrayList<GuestMessage2>();
list2.add(new GuestMessage2(1, "안녕", new Date()));
list2.add(new GuestMessage2(2, "HELLO", new Date()));
list2.add(new GuestMessage2(3, "빠이", new Date()));
return new GuestMessageList2(list2);
}
}package com.aia.firstspring.domain;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
public class GuestMessage2 {
private int id;
private String message;
private Date regDate;
public GuestMessage2() {
}
public GuestMessage2(int id, String message, Date regDate) {
this.id = id;
this.message = message;
this.regDate = regDate;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public Date getRegDate() {
return regDate;
}
public void setRegDate(Date regDate) {
this.regDate = regDate;
}
}
package com.aia.firstspring.domain;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
public class GuestMessageList2 {
private List<GuestMessage2> message;
public GuestMessageList2(List<GuestMessage2> message) {
this.message = message;
}
public List<GuestMessage2> getMessage2() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage2(List<GuestMessage2> message) {
this.message = message;
}
public GuestMessageList2() {
}
}